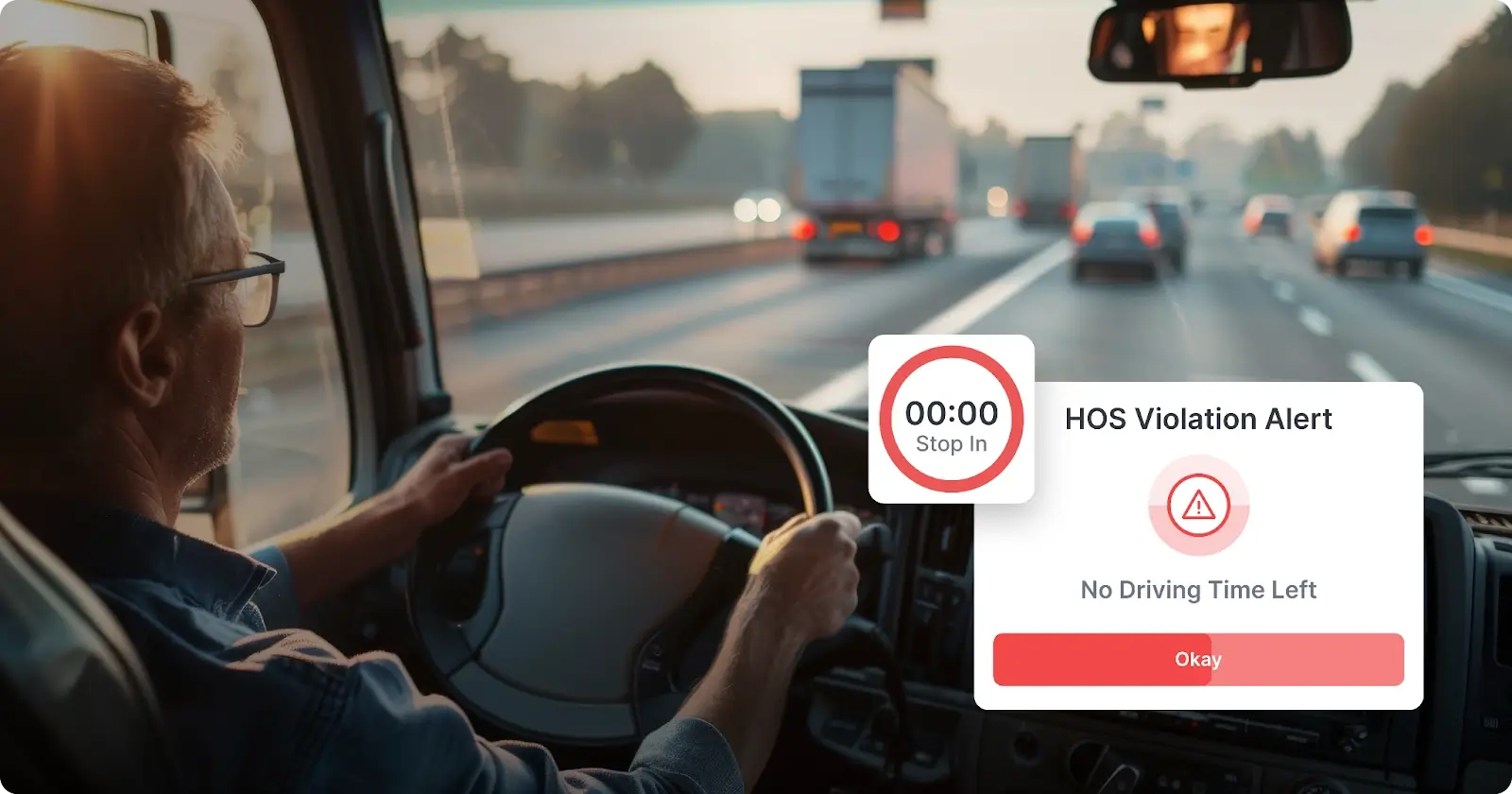
When it comes to managing a fleet of trucks, understanding and complying with Hours of Service (HOS) regulations is not just a legal obligation—this is essential for keeping your business running smoothly and your drivers safe on the road. At TruckX, we understand the challenges that fleets face, and we are here to help you navigate these regulations with ease through our ELD compliance and Fleet Management solutions.
In this blog, we will break down what the US HOS rules are, who needs to follow them, and how many hours the driver can legally drive each day. We will also look into how these rules differ from those in Canada, so you can stay compliant whether the routes are domestic or cross-border.
What are US HOS Rules?
Hours of Service (HOS) rules are a set of regulations established by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) to manage the working hours of commercial drivers in the United States. The FMCSA hours of service’s primary purpose of these regulations is to ensure road safety by preventing driver fatigue, a major cause of accidents involving commercial vehicles.
HOS regulations specify the maximum number of hours a driver can be on duty, the number of hours they can drive, and the minimum rest periods required between shifts. These rules are crucial not just for legal compliance but also for protecting the well-being of the drivers and the public.
Who Is Subject to HOS Regulations?
HOS regulations apply to most commercial motor vehicle (CMV) drivers in the United States. The drivers are subject to these rules if the fleet includes vehicles used for transporting goods or passengers across state lines, or if the vehicle’s gross weight exceeds 10,001 pounds. But the scope of HOS rules goes beyond just weight and distance.
1. Property-Carrying Drivers
For fleets involved in transporting goods, HOS rules are strict. These drivers must adhere to specific dot regulations regarding how many hours they can drive and how much rest they need between shifts. Compliance is non-negotiable, and failure to meet these requirements can result in hefty fines and even suspension of operations.
2. Passenger-Carrying Drivers
Drivers who transport passengers, such as in buses or shuttles, are also subject to HOS regulations. However, the rules differ slightly to account for the unique demands of passenger transport. For example, these drivers have a maximum driving limit of 10 hours after eight consecutive hours off duty, which is different from the rules for property-carrying drivers.
How Many Hours Can You Drive in a Day
1. Maximum Driving Limits
Understanding the daily and weekly driving limits set by the FMCSA is key to managing your fleet effectively. These limits are designed to prevent driver fatigue and ensure that all drivers get adequate rest between shifts.
2. 14-Hour Duty Limit
The 14-hour duty limit is one of the core components of HOS regulations. Once a driver begins their workday, they have a new 14-hour rule for truck drivers in which they can drive up to 11 hours. This window starts as soon as the driver goes ON-Duty, regardless of whether they are driving or performing other work-related tasks.
For instance, if a driver starts their day at 7:00 AM, their 14-hour window ends at 9:00 PM. They can only drive for a maximum of 11 hours within this period, and the remaining time must be used for rest limits, and various OFF-Duty breaks i.e. getting lunch, mandatory rest limit, etc.
3. 11-Hour Driving Limit
Within the 14-hour duty period, drivers are allowed to drive for a maximum of 11 hours. This driving limit is strictly enforced to ensure that drivers have enough time to rest and recharge before hitting the road again. After driving for 11 hours, the driver must take a mandatory rest period before starting another shift.
4. 60/70-Hour Duty Limit
The FMCSA also imposes limits on the total number of hours a driver can work in a week. There are two options: the 60-hour/7-day rule and the 70-hour/8-day rule. Under the 60-hour/7-day rule, a driver cannot drive after accumulating 60 ON-Duty hours over 7 consecutive days. Similarly, the 70-hour/8-day rule limits driving after 70 ON-Duty hours in 8 consecutive days.
These cumulative limits are essential for preventing driver fatigue, which can build up over several days or weeks.
5. Required Breaks and Rest Periods
In addition to driving limits, HOS regulations mandate specific breaks and rest periods to ensure that drivers get adequate rest. Drivers must take a 30-minute break after 8 consecutive hours of driving. This break can be taken at any time during the 14-hour duty window and is designed to prevent fatigue during long shifts.
Moreover, after completing a 14-hour duty period, drivers are required to take a 10-hour OFF-Duty period before they can start a new workday. This rest period allows drivers to recover and be fully alert when they return to the road.
Who is Exempt from HOS?
1. Short-Haul Operations
One of the most common exemptions is for short-haul drivers. Drivers who operate within a 150-mile radius of their reporting location and return to that location within 14 hours are exempt from some of the stricter HOS requirements. This exemption is particularly useful for local delivery drivers and regional operations that do not engage in long-haul trucking. The key conditions for this exemption include:
- Operating within a 150-mile radius.
- Completing the drive within a 14-hour period.
- Not requiring a commercial driver’s license (CDL) if the vehicle is under the CDL weight threshold.
2. Non-CDL Vehicles
Drivers who do not require a commercial driver’s license (non-CDL vehicles) are exempt from HOS regulations. Particularly if the vehicle is used for personal use or small-scale business operations. These exemptions typically apply to vehicles under 10,000 pounds or those used in intrastate commerce, depending on state regulations.
3. Other Exemptions
Various other exemptions might apply depending on the nature of the operation or the type of vehicle being used. For example:
- Driveaway-Towaway Operations: If a driver is delivering an empty vehicle, the HOS rules might be relaxed.
- Adverse Driving Conditions: Drivers can extend their driving time by up to two hours if they encounter unforeseen adverse driving conditions like heavy traffic or severe weather.
How Are US HOS Rules Different from Canadian HOS Rules
If the fleet operates across the US-Canada border, it’s crucial to understand the differences between US and Canadian HOS rules. While both sets of regulations aim to prevent driver fatigue and ensure road safety. There are notable differences in how they are implemented.
1. Differences in Driving Limits in HOS
In Canada, drivers are allowed to drive for up to 13 hours within a 16-hour workday, compared to the 11-hour limit within a 14-hour workday in the US. This difference gives Canadian drivers more flexibility, but it also requires careful management to ensure compliance when crossing the border.
2. Differences in Rest Requirements
Canadian HOS rules also differ in their approach to rest periods. In Canada, drivers must take a mandatory 8-hour OFF-Duty period. After reaching their daily driving limit, compared to the 10-hour OFF-Duty period required in the US. Additionally, Canadian drivers must take a 24-hour OFF-Duty period. After accumulating 70 hours of work in seven days, the US has a 34-hour restart rule.
3. Regulatory Authorities and Enforcement
While the FMCSA oversees HOS regulations in the US. Canadian Council of Motor Transport Administrators (CCMTA) is responsible for HOS rules in Canada. These authorities have different approaches to enforcement, and penalties for non-compliance can vary significantly. For fleets operating in both countries, understanding these differences is key to avoiding fines and ensuring smooth operations.
Manage HOS Using TruckX ELD One
1. Easy Setup and Integration
FMCSA-Approved TruckX ELD One is engineered for quick and straightforward installation, making it accessible even for those with non-technical expertise. The device plugs directly into your vehicle’s diagnostic port, automatically syncing with the TruckX mobile app. This seamless integration ensures that your HOS data is recorded in real-time without the need for manual entries, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring accurate compliance records.
2. Automated HOS Logging
Once connected, TruckX ELD One automatically tracks your driving hours, ON-Duty time, and rest periods according to FMCSA regulations. The system continuously tracks your vehicle’s movements, capturing data such as engine status, speed, and location. This data is then used to automatically update your HOS logs, eliminating the need for paper logs and manual calculations.
- Real-Time Data Sync: As your drivers go about their day, TruckX ELD One records every movement in real-time, ensuring that your logs are always up-to-date.
- Automatic Duty Status Changes: The system detects when your vehicle is in motion and automatically switches the duty status from “OFF-Duty” to “Driving,” making it easy to maintain accurate records.
- Violation Alerts: TruckX ELD One will alert drivers and fleet managers if they are approaching a violation of HOS rules, allowing them to take corrective action before a violation occurs.
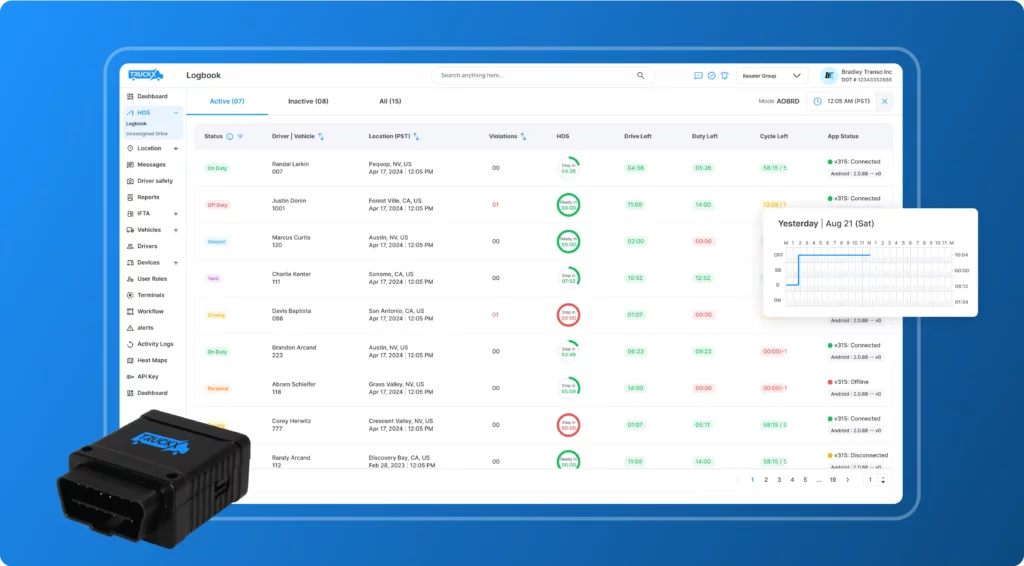
3. User-Friendly Dashboard
TruckX ELD One comes with a user-friendly dashboard that provides both drivers and fleet managers with a clear overview of HOS status. This dashboard can be accessed via the TruckX Driver or Fleet app, offering flexibility and convenience for tracking compliance.
- Driver Logs: Drivers can easily view and edit their logs through the app, ensuring that all information is correct before submitting their records.
- Fleet Manager Oversight: Fleet managers can access a comprehensive view of all drivers’ HOS logs, helping them identify trends, spot potential issues, and ensure compliance across the fleet.
Conclusion
Understanding and complying with Hours of Service rules is crucial for any fleet operating in the United States. These rules are designed to prevent driver fatigue, reduce accidents, and ensure the safety of everyone on the road. By familiarizing yourself with the specific requirements for the fleet and taking advantage of any applicable exemptions, you can optimize operations while staying compliant.
At TruckX, we offer comprehensive ELD Compliance and Fleet Management solutions tailored to the needs of owner-operators to the large fleets. Our device is designed to help you navigate the complexities of HOS regulations, ensuring that the fleet operates safely, efficiently, and within the bounds of the law.